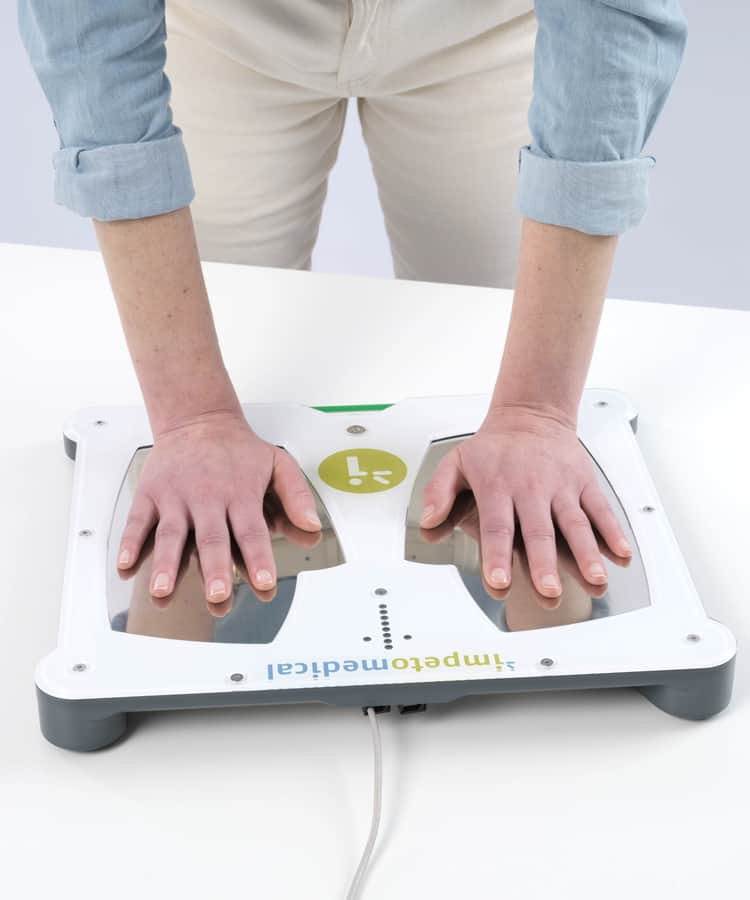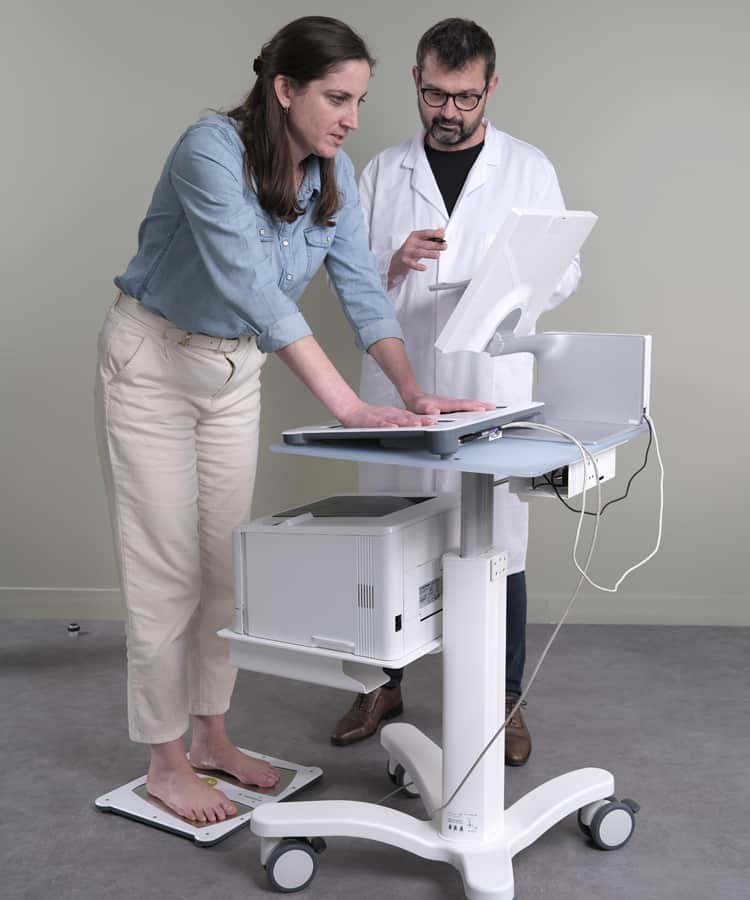
SUDOSCAN has demonstrated its efficacy in the field of oncology
Peripheral neuropathy is the result of damage to peripheral nerves, including small fiber neuropathy involving small and myelinated nerves (Aδ), as well as unmyelinated nerves (unmyelinated C fibers). In peripheral neuropathy, small somatic and autonomic fibers can be affected. Small fibers control thermal perception, pain perception, and autonomic functions such as cardiac, pulmonary or enteric functions [1].
Peripheral neuropathy can be a complication of several diseases such as diabetes, neurological or metabolic disorders, and infections. It can also result from certain drugs such as chemotherapy or alcohol consumption.
This complication can occur in the very early stages of disease. Its detection may help physicians to better manage their patients and avoid advanced complications.
In the field of oncology, SUDOSCAN has demonstrated its clinical utility to detect chemotherapy induced polyneuropathy (CIPN). This can help the physician to manage treatment and limit neuropathy worsening, thus improving the quality of life of the patients receiving chemotherapy or in palliative care.
Find the main publication list on using SUDOCAN in oncology click here.
Detection of painful oxaliplatin-induced peripheral neuropathy can be easily performed with SUDOSCAN to help treatment management [2]
Oxaliplatin-induced peripheral neuropathy (OIPN) has been assessed using SUDOSCAN in a study conducted by Delmotte et al from Saint Joseph Hospital, Paris. The aim of the prospective study was to investigate how Electrochemical Skin Conductance (ESC, measured with SUDOSCAN) could be helpful in diagnosing OIPN.
36 patients with cancer, treated for at least three months with oxaliplatin, and suffering from clinical OIPN were included. Low ESC measurements signal decreased sudomotor nerve function, while a Neuropathic Pain Symptom Inventory (NPSI) score greater than 0 indicates painful symptoms.
The main result was the correlation between the NPSI score and ESC scores in the hands (rho value = -0.69, p less than 0.0001) and feet (rho value = -0.79, p less than 0.0001). ESC values were lower in neuropathic patients with painful symptoms than in those without painful symptoms (p = 0.0003 and p less than 0.0001 for hands and feet, respectively).
These preliminary data suggest that ESC measured with SUDOSCAN could be a useful objective marker of painful oxaliplatin-induced neuropathy and could complement the use of subjective clinical scales.
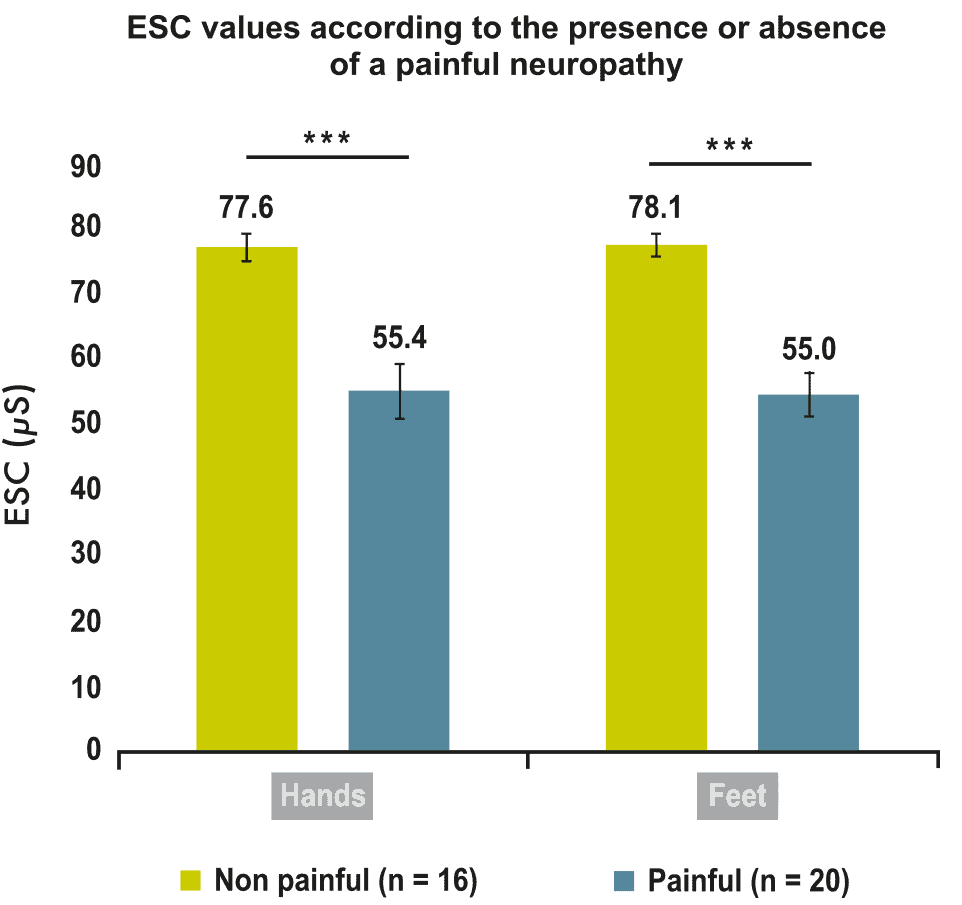
SUDOSCAN Benefits

Fast
No patient preparation
Results in 3 minutes
Easy-to-read critical data points to help physicians reach a diagnosis

Secure
Non-invasive
No fasting
Easy to operate
CE and FDA approvals

Accurate
Reproducible quantitative results
Independent from environmental conditions
Backed by evidence-based research
150 peer-reviewed journals publications
References
[1] Levine TD. Small Fiber Neuropathy: Disease Classification Beyond Pain and Burning. J Cent Nerv Syst Dis. 2018;10:1179573518771703. Published 2018 Apr 18.[2] Delmotte J.B et al. Electrochemical Skin Conductance as a Marker of Painful Oxaliplatin-Induced Peripheral Neuropathy. Neurol Res Int. 2018; 2018: 1254602.




