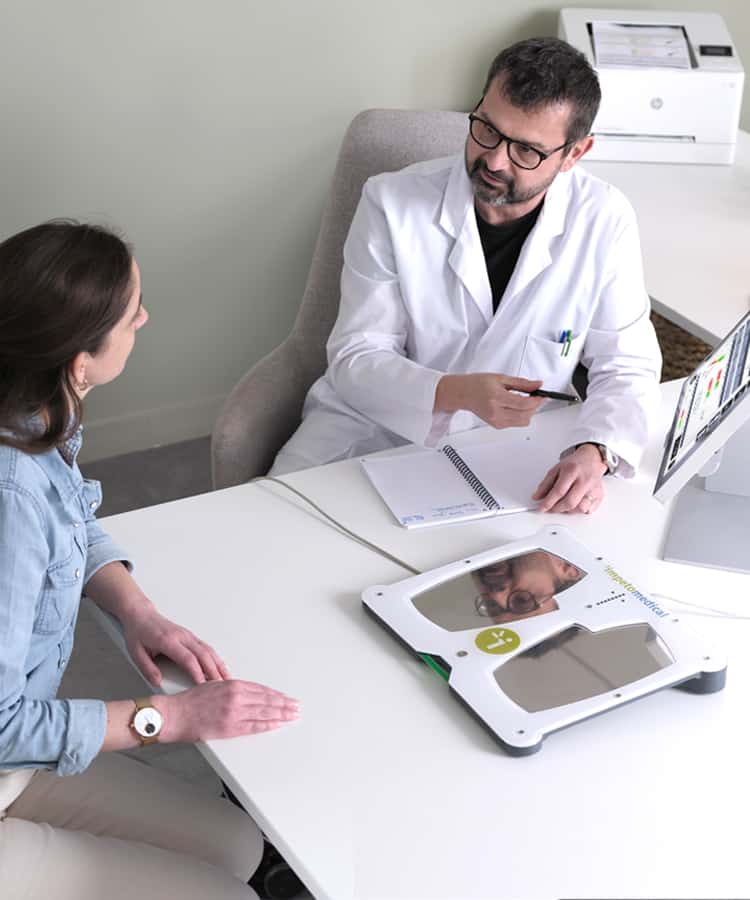
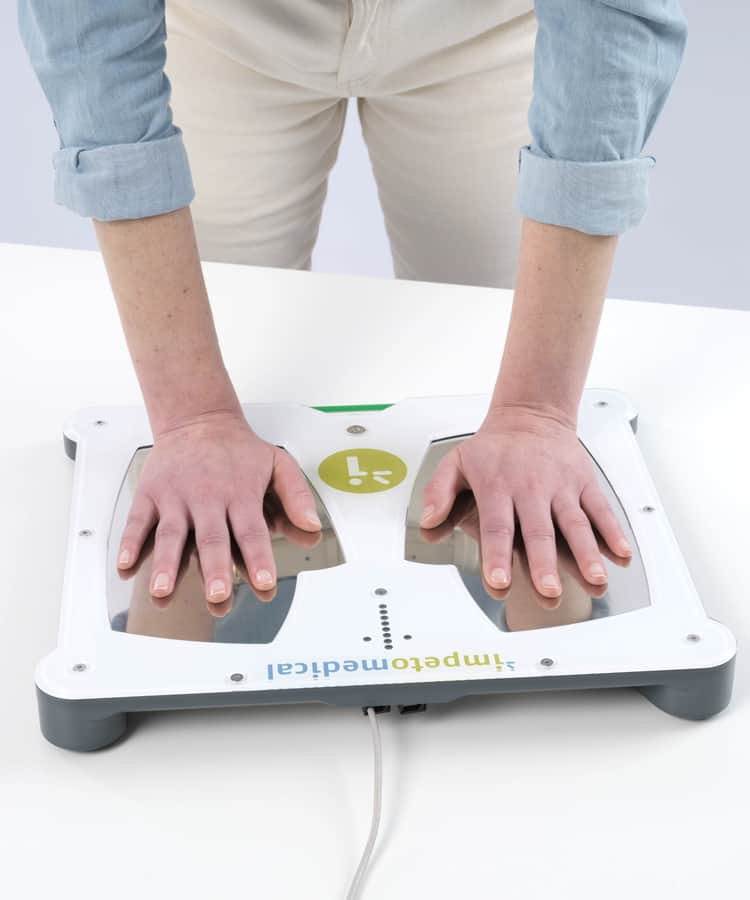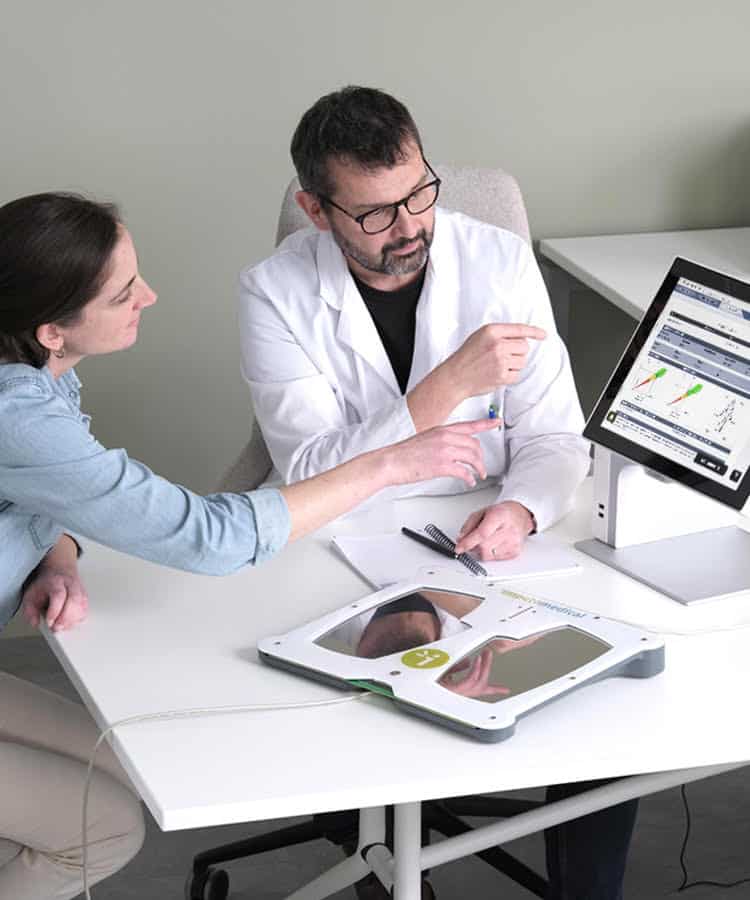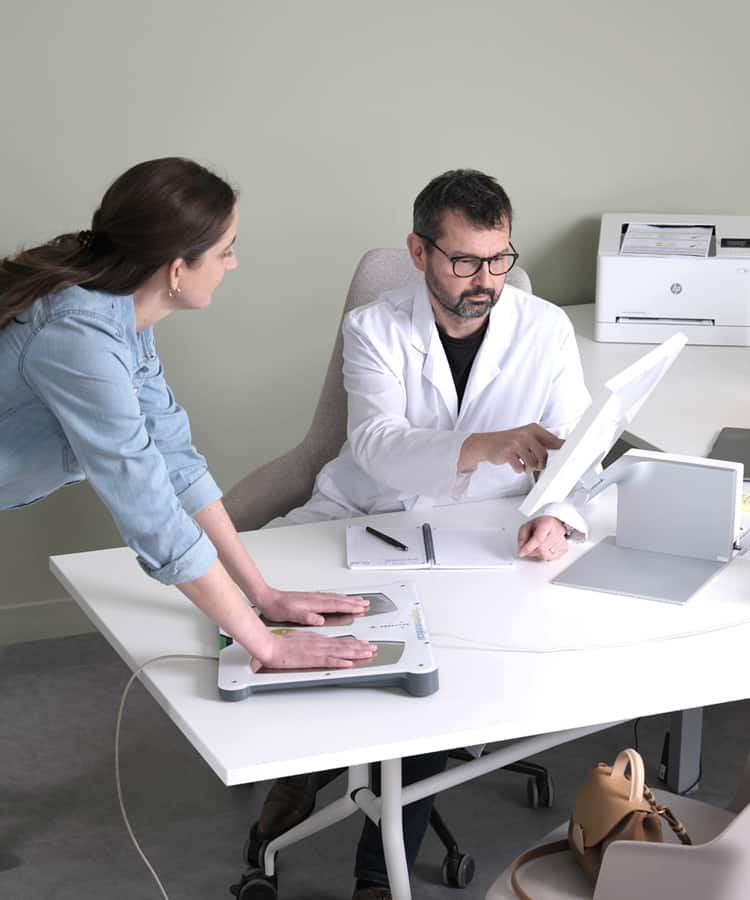
SUDOSCAN has demonstrated its efficacy in the field of neurology
Peripheral neuropathy is the result of damage to peripheral nerves, including small fiber neuropathy involving small and myelinated nerves (Aδ), as well as unmyelinated nerves (unmyelinated C fibers). In peripheral neuropathy, small somatic and autonomic fibers can be affected. Small fibers control thermal perception, pain perception, and autonomic functions such as cardiac, pulmonary or enteric functions [1].
Peripheral neuropathy can be a complication of several diseases such as diabetes, neurological or metabolic disorders, and infections. It can also result from certain drugs or alcohol consumption.
This complication can occur in the very early stages of disease. Its detection may help physicians to better manage their patients and avoid advanced complications.
Small fiber neuropathies have been assessed using SUDOSCAN in different diseases and therapeutic areas. The following are some of the diseases with neurological complications where SUDOSCAN has been applied:
- Hereditary amyloidosis, AA, wild type
- Covid-19
- Hepatitis C
- Epilepsy
- Fabry disease
- Parkinson’s disease
- Autoimmune small fiber neuropathy
- Fibromyalgia
- Lewy body dementia
- Narcolepsy
- Sjörgen’s syndrome
- Pure autonomic failure
Find the main publication list of diseases with related neurological complications click here.

Clinical application of SUDOSCAN in wild-type cardiac amyloidosis
Amyloidosis is an acquired or hereditary rare disease caused by amyloid protein deposits in organs. Several types have been reported including transthyretin hereditary amyloidosis (hATTR amyloidosis or familial amyloidosis), wild-type cardiac amyloidosis, AA amyloidosis and AL amyloidosis.
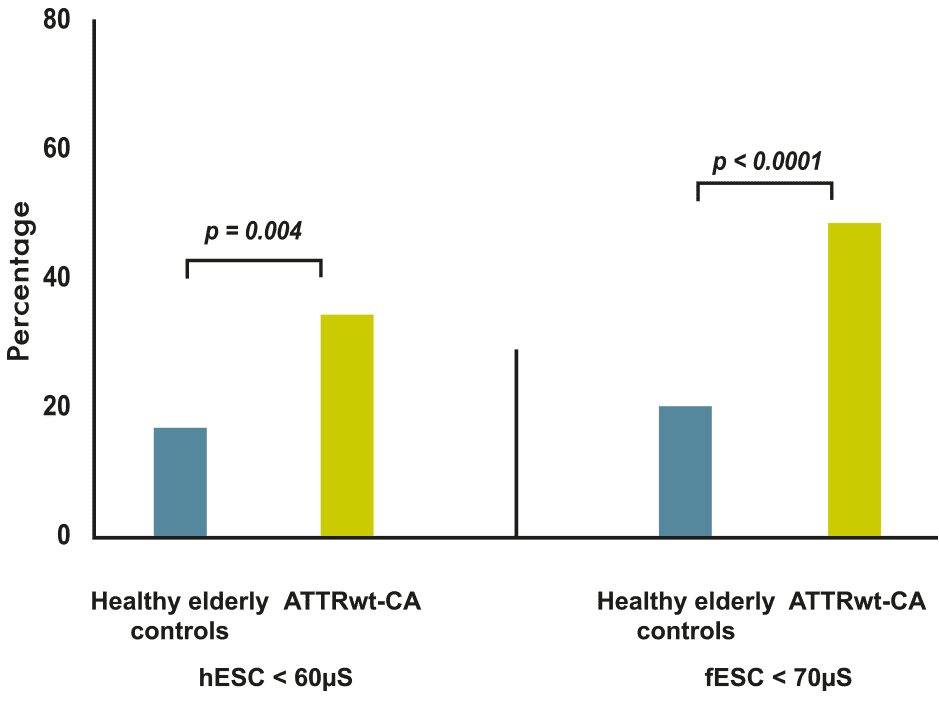
M. Kharoubi from Henri Mondor University Hospital, Paris, Pr T. Damy’s team, has published in ESC Heart Failure [2] results on screening for autonomic neuropathy in transthyretin wild-type cardiac amyloidosis (ATTRwt-CA), using SUDOSCAN. She demonstrated that SUDOSCAN feet measures (electrochemical skin conductance, ESC) were reduced in almost 50% of patients with ATTRwt-CA and were associated with a worse prognosis, thus helping identify patients at higher risk for a poor outcome. These findings in cardiac amyloidosis highlight the functional interest of SUDOSCAN in daily cardiology practice. SUDOSCAN testing could be completed by cardiologists and would allow patients with ATTRwt-CA and poor ESC to be triaged for consultation with a neurologist for further investigation, thus optimizing the management and monitoring of these patients.
Sudoscan correlates with skin biopsy for the detection
of small fiber neuropathy [2]
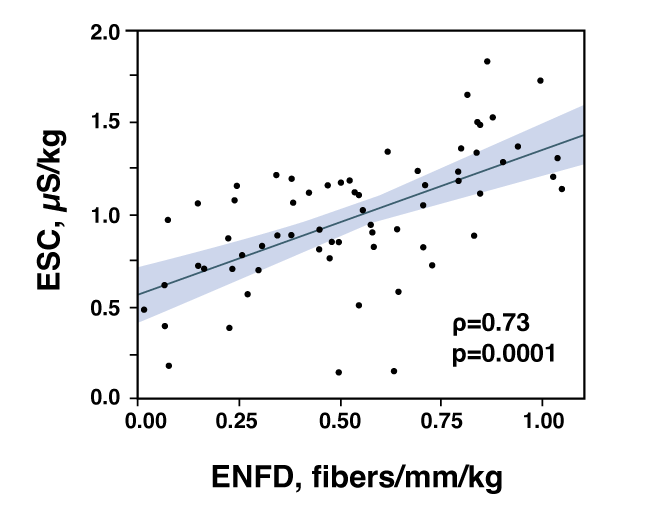
Professor Novak from University of Massachusetts Medical School investigated the correlation between electrochemical skin conductance (ESC) at the feet and results of skin biopsies including epidermal nerve fiber density (ENFD) and sweat gland nerve fiber density (SGNFD) at the distal leg.
In this study, conducted on 81 patients, ESC was diminished in subjects who had a reduced number of small fibers in the skin and the ESC reduction was proportional to ENFD and SGNFD making from Sudoscan a valuable tool in detecting loss of small nerve fibers.
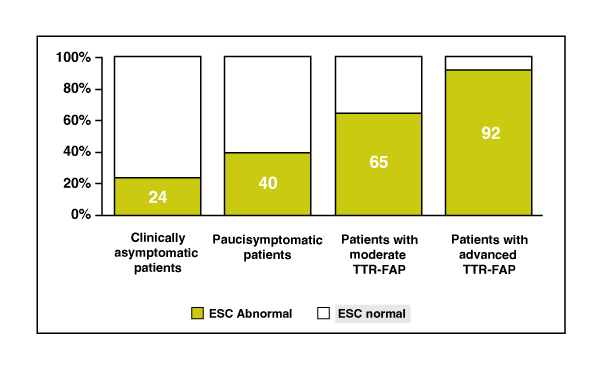
Sudoscan detects polyneuropathy within asymptomatic amyloidosis patients allowing better disease management [3]
Professor Jean-Pascal Lefaucheur et al. have evaluated the value of ESC measurement by SUDOSCAN to assess the distal involvement of small autonomic fibers in familial amyloid polyneuropathy (FAP) due to various transthyretin (TTR) mutations.
ESC was measured at both hands and feet in 126 patients with either Val30Met (n = 65) or non-Val30Met (n = 61) TTR mutation. This series included clinically asymptomatic (n = 21) and paucisymptomatic (n = 30) patients, as well as patients with moderate (n = 37) or advanced (n = 38) TTR-FAP.
ESC was reduced in 24% of clinically asymptomatic patients, 40% of paucisymptomatic patients, 65% of patients with moderate TTR-FAP, and 92% of patients with advanced TTR-FAP.
Accordingly, ESC measures well correlated with the severity of TTR-FAP and could provide early marker of the disease.
Sudoscan is an easy, convenient and reliable method to diagnose small fiber neuropathy: comparative study of 5 neurophysological tests [4]
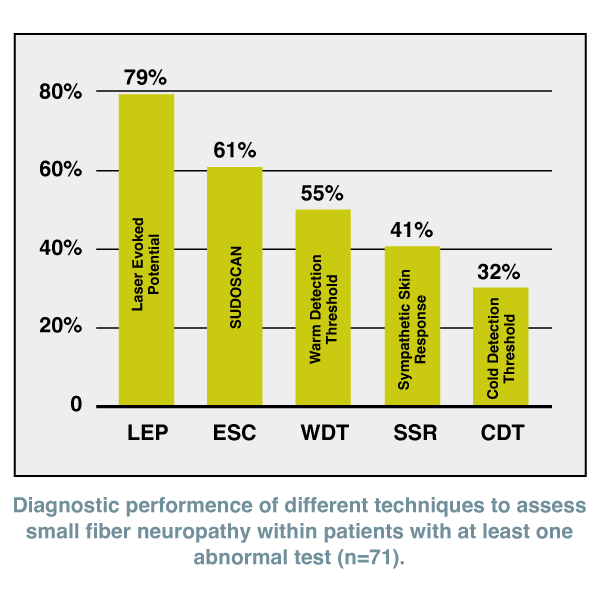
Prof. Jean-Pascal Lefaucheur et al. compared the effectiveness of five small fiber neuropathy tests in 87 patients with clinically definite or possible SFN from various causes.
The tests included quantitative sensory testing with determination of warm and cold detection thresholds (WDT, CDT), recording of laser-evoked potentials (LEP) and sympathetic skin responses (SSRs), and measurement of electrochemical skin conductance (ESC) using SUDOSCAN.
SUDOSCAN Benefits

Fast
No patient preparation
Results in 3 minutes
Easy-to-read critical data points to help physicians reach a diagnosis

Secure
Non-invasive
No fasting
Easy to operate
CE and FDA approvals

Accurate
Reproducible quantitative results
Independent from environmental conditions
Backed by evidence-based research
150 peer-reviewed journals publications
References
[1] Levine TD. Small Fiber Neuropathy: Disease Classification Beyond Pain and Burning. J Cent Nerv Syst Dis.2018;10:1179573518771703. Published 2018 Apr 18.[2] Kharoubi M, Roche F, Bézard M, Hupin D, Silva S, Oghina S, Chalard C, Zaroui A, Galat A, Guendouz S, Canoui-Poitrine F, Hittinger L, Teiger E, Lefaucheur JP, Damy T. Prevalence and prognostic value of autonomic neuropathy assessed by Sudoscan® in transthyretin wild-type cardiac amyloidosis. ESC Heart Fail. 2021 Apr;8(2):1656-1665.
[2] P. Novak. Electrochemical Skin Conductance Correlates with Skin Nerve Fiber Density. Frontiers in Aging Neuroscience, August 2016|Volume8|Article199.
[3] Lefaucheur JP et al. The value of electrochemical skin conductance measurement using Sudoscan_ in the assessment of patients with familial amyloid polyneuropathy. Clinical Neurophysiology 129 (2018) 1565–1569.
[4] AJ.P Lefaucheur et al. Diagnosis of small fiber neuropathy: A comparative study of five neurophysiological tests. Neurophysiol Clin. 2015 Dec;45(6):445-55.





