SUDOSCAN in Oncology :
Chemotherapy InduCed Polyneuropathy
Two studies evaluating SUDOSCAN
Severe drug-induced neurotoxic adverse effects constitute the second most common cause of dose limitation after haematological adverse effects. Chemotherapy Induced Polyneuropathy (CIPN) is commonly associated with platinum analogues, antitubulins (taxane), the proteasome inhibitor bortezomib, and thalidomide. However, it is poorly investigated at an early stage due to the lack of
a simple assessment tool.
As sweat glands are innervated by small autonomic C-fibers, sudomotor function testing has been suggested for early screening of peripheral neuropathy.
Two important studies have evaluated SUDOSCAN performances in the detection and follow-up of CIPN.
Quick, non-invasive and quantitative assessment of small fiber neuropathy in patients receiving chemotherapy
Saad M, Psimaras D, Tafani C, Sallansonnet-Froment M, Calvet JH, Vilier A, Tigaud JM, Bompaire F, Lebouteux M, de Greslan T, Ceccaldi B, Poirier JM, Ferrand FR, Le Moulec S, Huillard O, Goldwasser F, Taillia H, Maisonobe T, Ricard D.
J Neurooncol. 2016 Apr;127(2):373-80.
Background: The Total Neuropathy Score clinical version (TNSc) explores large and small fibers neuropathy, with a score that ranges from 0 to 28 with a higher sensitivity than other scales. TNSc is
a seven item composite clinical neuropathy scale that includes symptoms, signs and ability is a validated and reliable CIPN scale. To date this scale seems to be the best compromise between reliability and simplicity but is not completely objective and requires training.
Aim: compare SUDOSCAN and TNSc in the assessment of CIPN.
Methods: 88 patients receiving at least two infusions of Oxaliplatin only (45.4 %), Paclitaxel only (14.8 %), another drug only (28.4 %) or two drugs (11.4 %) were enrolled in the study. At each chemotherapy infusion the accumulated dose of chemotherapy was calculated, TNSc and SUDOSCAN were carried out.
Results: For patients receiving Oxaliplatin mean hands ESC changed from 73 ± 2 to 63 ± 2 and feet ESC from 77 ± 2 to 66 ± 3 µS (p<0.001) while TNSc changed from 2.9 ± 0.5 to 4.3 ± 0.4. Similar results were observed in patients receiving Paclitaxel or another neurotoxic chemotherapy. During the follow-up, ESC values of both hands and feet with a corresponding TNSc < 2 were 70 ± 2 and 73 ± 2µS respectively while they were 59 ± 1.4 and 64 ± 1.5 µS with a corresponding TNSc > 6 (p<0.0001 and p = 0.0003 respectively).
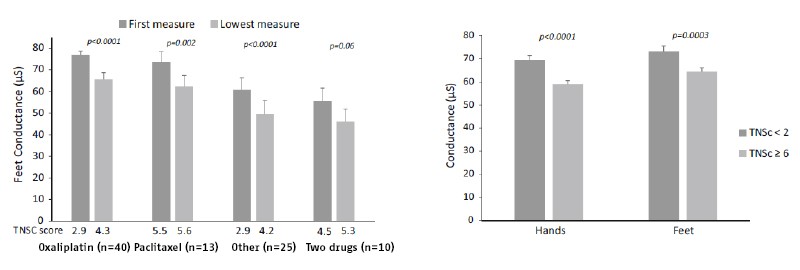
Comparison of hands and feet conductance according to TNSc extreme values (data is mean ± SEM); in patients receiving oxaliplatin, paclitaxel or other drugs alone or in combination (n=61)
Conclusion: This preliminary study suggests that small fiber neuropathy could be screened and followed using SUDOSCAN in patients receiving chemotherapy.
Electrochemical Skin Conductance as a Marker of Painful Oxaliplatin-Induced Peripheral Neuropathy
Delmotte JB, Tutakhail A, Abdallah K, Reach P, D’Ussel M, Deplanque G, Beaussier H, Coudoré F.
Neurology Research International. Volume 2018, Article ID 1254602.
Backround and aim: Oxaliplatin is a platinum compound widely used in gastrointestinal cancer treatment but produces dose-limiting peripheral neuropathy. New insights into oxaliplatin-induced peripheral neuropathy (OIPN) assessment are needed to detect more effectively this condition. In this context, Canaloxa study was conducted, a prospective preliminary clinical trial that aimed to investigate how Electrochemical Skin Conductance (ESC), a parameter used in small fiber neuropathy assessment, could be helpful in OIPN diagnosis.
Methods: Cancer patients treated for at least three months with oxaliplatin and suffering from clinically OIPN were included. Electrochemical Skin Conductance, thermal thresholds, and neuropathic pain using NPSI (Neuropathic Pain Symptom Inventory) were assessed in all included patients.
Results: During one year, 36 patients were included. The main result was the correlation between ESC and Neuropathic Pain Symptom Inventory score for hands (rho value = -0.69, p < 0.0001) and feet (rho value = -0.79, p < 0.0001). ESC values were lower in neuropathic patients with painful symptoms than in ones without painful symptoms 55.4 ± 19.7 vs 77.6± 7.9 (p = 0.0003) for hands and 55.0 ± 15.0 vs 78.1± 6.6 (p < 0.0001) for feets.
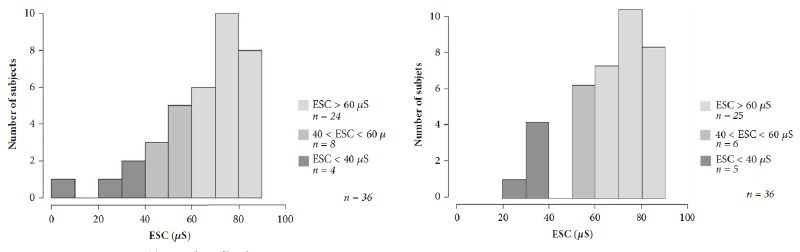
ESC values of hands
ESC values of feet
Conclusion: ESC could be a useful objective marker of painful oxaliplatin-induced neuropathy and could complement the use of subjective clinical scales.






