Sudomotor dysfunction in patients
recovered from COVID-19
Anand Hinduja, Abdul Moutairou, Jean-Henri Calvet
Article title: Sudomotor dysfunction in patients recovered from COVID-19.
Neurophysiologie Clinique/Clinical Neurophysiology, Feb 2021.
Dysautonomia has been reported in COVID-19 infection. Very recently an observational study, performed by Hinduja et al, from Aarti Clinic, Kharghar, Navi Mumbai, India, involved 50 patients who had recovered from COVID-19 and were seen within 3 months post-infection in an outpatient clinic for fatigue or various neurological symptoms.
The NHS (National Health Service) questionnaire for neurological symptoms was completed and electrochemical skin conductance was measured using SUDOSCAN.
Presence of sweat dysfunction (decrease in FESC – Feet Electrochemical Skin Conductance) was observed in 26% of patients, while 6% had severe sweat dysfunction.
These patients with decrease in FESC more frequently reported at least one motor, sensory or autonomic symptom (p = 0.04). See Table 1.
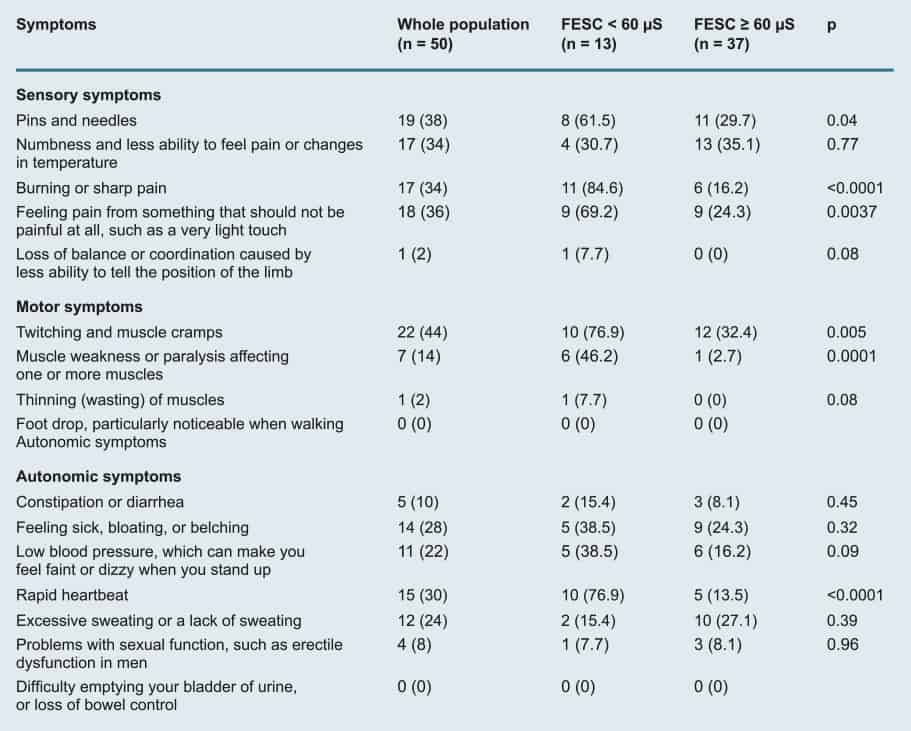
Table 1: Details of symptoms (sensory, motor and autonomic) reported by the patients
in the whole population and according to the presence (FESC <60 µS) or absence
of sudomotor dysfunction (FESC ≥60 µS).
This preliminary observational study reveals that more than 25 % of patients who recovered from COVID-19 and seen in an outpatient clinic, had sweat dysfunction generally reflecting dysautonomia, which could have severe consequences and must be monitored during follow-up.
These findings must be confirmed in a larger population with additional testing but underline the necessity of enhancing screening of dysautonomia in this population of patients recovered from COVID-19.
In this way it could be helpful to test the patients recovered from COVID-19 using SUDOSCAN a very simple and rapid test.